We want to be successful with our decisions. Even though failure is often glamorized, nobody wants it on purpose. Everyone wishes to be successful when they’re starting a company, launching a product, hiring a leader or even while buying a house.
It may sound obvious, but the bedrock of good decisions is defining what good means before you execute on a decision.
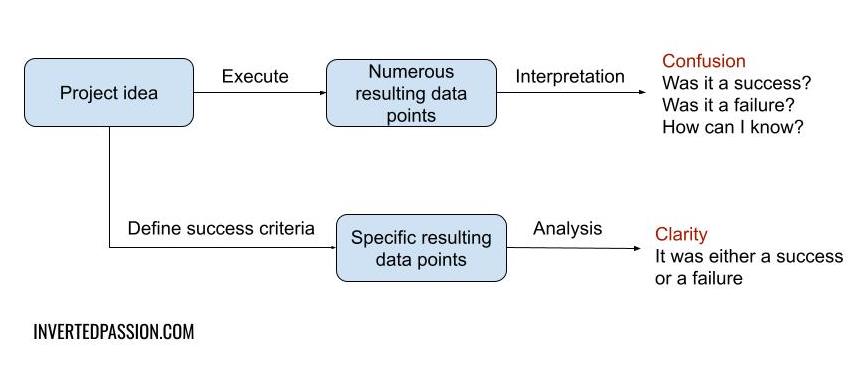
Here’s why it’s important to define a clear, objective and unambiguous criteria before making any decision. First, without a commitment to an objective criterion, your brain will latch onto your how you’re feeling to decide whether the outcome of the project is good or bad. These emotions are influenced by all sorts of subconscious cognitive biases. In the end, you will end up picking data points that support your emotional inclination while ignoring the other data points. ...

